
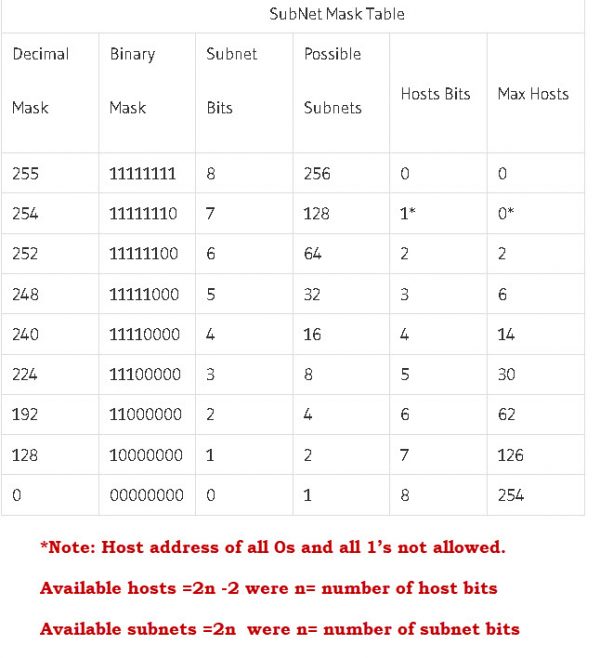
Step 5 – Calculate What Subnet Mask to UseĢ56 minus the block size is what gives you the subnet mask.Ģ56 – 4 = 252 which is equal to the prefix /22 Now that we have calculated the number of subnets required, we move to the next step. From the finger table 1.1 we know that 2 raised to the power of 6 gives us 64 subnets which is more than enough for our needs. In this example you have been asked to provision 60 subnets. Step 4 – Calculate and provision the number of subnets required.
#Class a subnet mask table full
Step 3 – Write down the full address with the prefix Step 2 – Write down the default subnet mask The above address belongs to the Class B IP Address Group – Class B(128-191) as 172 falls within that range of addresses. The first thing is to check what private ip address class the given address belongs to. Subnetting Question 1: We have an address 172.18.0.0 and we need 60 subnets. You are usually given a subnet address and asked to provision a number of subnets.
Write down the Class it belongs to | Is it Class A, B, or C ?Īs a network engineer, as part of design or expansions you may from time to time be required to provision a number of subnets based on an Subnet ID.

Firstly classify the address | This is exactly what we did in the exercise above.Step by Step Guide to Understanding IP Subnetting – The Process for Subnetting Learn this table | Finger Table 1.1 Finger How was that exercise? Let us move on to understanding subnetting with this step by step guide. Step by Step Guide to Understanding IP Subnetting -What Class does each IP below belong to? Referencing the above table, can you perform a detective work in identifying which class the following ip addresses belong? It is like knowing the Periodic Table in Chemistry. It is extremely important to remember this table as it is a required knowledge for every subnetting task you may encounter. Step by Step Guide to Understanding IP Subnetting – Private IP Address Classes Table This tutorial will take you through the best way in calculating subnetting requirements. You may not always have the subnet address or mask to identify what the ip address is. In this article on the Step by Step Guide to Understanding IP Subnetting, I attempt to start from the basics all the way to solving any subnetting questions with an approach that is reliably accurate at all times.

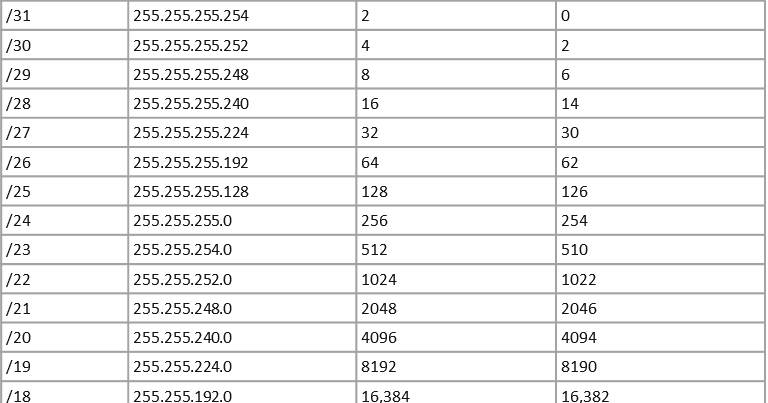
The article also indicated provisioned subnet mask information which made it simple for the network engineer to carry out subnetting. Below is given all possible combination of Class B subnetting − Class C SubnetsĬlass C IP addresses are normally assigned to a very small size network because it can only have 254 hosts in a network.In my previous article, I showed you a smarter way to solve subnetting questions but that was quite an intermediate approach as I expected some prior understanding. Class B IP Addresses can be subnetted the same way as Class A addresses, by borrowing bits from Host bits. Class B Subnetsīy default, using Classful Networking, 14 bits are used as Network bits providing (2 14) 16384 Networks and (2 16-2) 65534 Hosts. Because these two IP addresses cannot be assigned to hosts, sub-netting cannot be implemented by using more than 30 bits as Network Bits, which provides less than two hosts per subnet. In case of subnetting too, the very first and last IP address of every subnet is used for Subnet Number and Subnet Broadcast IP address respectively. Given below is a list of all possible combination of Class A subnets − The Subnet mask is changed accordingly to reflect subnetting. To make more subnet in Class A, bits from Host part are borrowed and the subnet mask is changed accordingly.įor example, if one MSB (Most Significant Bit) is borrowed from host bits of second octet and added to Network address, it creates two Subnets (2 1=2) with (2 23-2) 8388606 Hosts per Subnet. In Class A, only the first octet is used as Network identifier and rest of three octets are used to be assigned to Hosts (i.e. By using subnetting, one single Class A IP address can be used to have smaller sub-networks which provides better network management capabilities.
Classful IP addressing does not provide any flexibility of having less number of Hosts per Network or more Networks per IP Class.ĬIDR or Classless Inter Domain Routing provides the flexibility of borrowing bits of Host part of the IP address and using them as Network in Network, called Subnet. Each IP class is equipped with its own default subnet mask which bounds that IP class to have prefixed number of Networks and prefixed number of Hosts per network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
